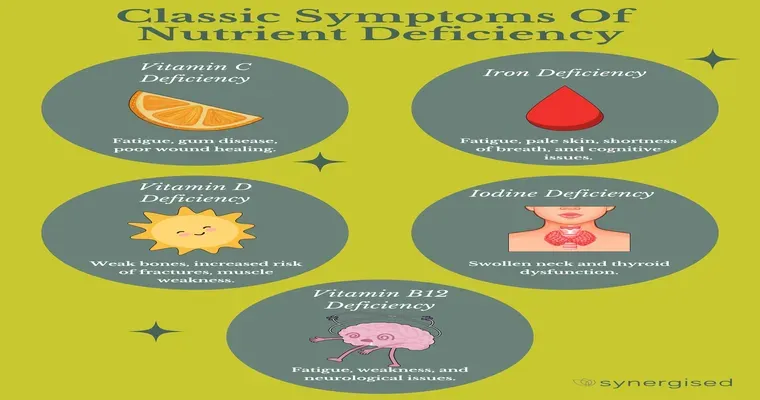
In recent years, the relationship between "cognitive issues" and "nutritional deficiency" has garnered significant attention in the fields of medicine and nutrition. Many studies suggest that a lack of essential nutrients can play a critical role in the development and progression of various cognitive impairments. From memory loss to difficulties in concentration, understanding this connection is vital for promoting mental health and overall well-being.
Understanding Cognitive Issues
Cognitive issues encompass a wide range of problems related to thinking, memory, and reasoning. These can include conditions such as dementia, Alzheimer's disease, and other forms of cognitive decline. Symptoms may range from mild forgetfulness to severe disruptions in daily functioning. As the global population ages, the prevalence of cognitive disorders is increasing, making it crucial to explore all potential contributing factors, including "nutrition".
The Role of Nutrition
Nutrition plays a fundamental role in maintaining brain health. The brain requires a variety of nutrients to function optimally. Key nutrients such as "omega-3 fatty acids", "B vitamins", "vitamin D", and "antioxidants" have been shown to support cognitive function. A deficiency in any of these nutrients can lead to impaired brain health, potentially exacerbating cognitive issues.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Omega-3 fatty acids, commonly found in fish and flaxseeds, are essential for maintaining neuronal function. Studies suggest that low levels of omega-3s are linked to cognitive decline and increased risk of developing neurodegenerative diseases. Incorporating these fatty acids into the diet may help protect against cognitive deterioration.
B Vitamins
B vitamins, particularly B12 and folate, are crucial for brain health. A deficiency in these vitamins can lead to elevated homocysteine levels, which are associated with an increased risk of cognitive impairment. Ensuring adequate intake of B vitamins through diet or supplementation can be a proactive measure for brain health.
Vitamin D
Vitamin D deficiency has also been linked to cognitive decline. Research indicates that individuals with low levels of vitamin D may be at a higher risk for developing conditions such as Alzheimer's disease. Sun exposure and certain foods like fatty fish and fortified products can help maintain adequate vitamin D levels.
Antioxidants and Cognitive Function
Antioxidants, found in fruits and vegetables, protect the brain from oxidative stress, which can harm brain cells. A diet rich in antioxidants may lower the risk of cognitive decline. Foods like berries, nuts, and leafy greens not only provide essential nutrients but also support overall brain health.
Conclusion
The connection between "cognitive issues" and "nutritional deficiency" is becoming increasingly clear. A well-balanced diet rich in essential nutrients is crucial for maintaining cognitive function and preventing decline. For individuals experiencing cognitive difficulties, addressing nutritional deficiencies could be a vital step towards improving mental health. As research continues to evolve, it is essential to recognize the importance of nutrition in supporting cognitive health and to prioritize a diet that fosters both physical and mental well-being.