As we age, personal "hygiene" can become a challenging issue, especially among the "elderly". Many older adults may resist maintaining proper hygiene practices due to various physical, cognitive, or emotional factors. Understanding how to address these challenges is crucial for caregivers and family members to ensure the health and well-being of older individuals. This article explores effective strategies for overcoming "hygiene resistance" in the elderly.
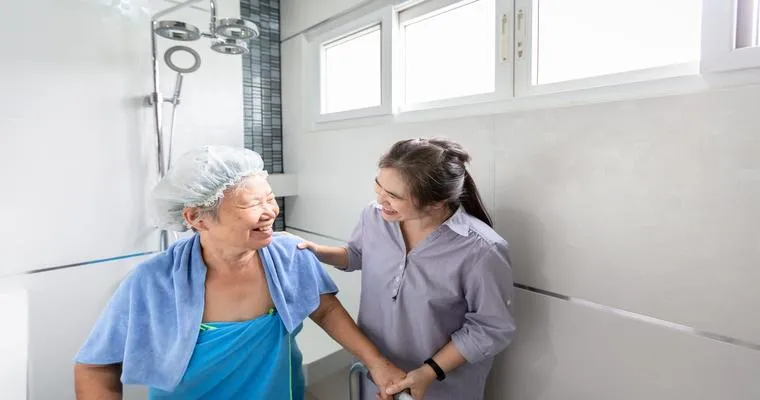
One of the primary reasons for hygiene resistance in the elderly is "physical limitations". Conditions such as arthritis, limited mobility, or chronic pain can make daily activities, like bathing and grooming, difficult to perform. Caregivers should assess the individual's physical capabilities and provide assistance when necessary. This might include using adaptive tools like grab bars, shower chairs, or long-handled sponges to make personal care easier and more comfortable.
Another factor contributing to hygiene resistance is "cognitive decline". Conditions such as dementia or Alzheimer's disease can impair an older person's memory and reasoning abilities, making it hard for them to understand the importance of maintaining personal hygiene. In such cases, it is essential to create a routine that is both simple and consistent. Using visual cues, such as charts or reminders, can help reinforce hygiene habits, while gentle prompts can encourage participation without causing frustration.
Emotional and psychological factors also play a significant role in hygiene resistance. Feelings of shame or embarrassment about physical changes can lead to avoidance of personal care routines. To combat this, caregivers should approach the topic with sensitivity and compassion. Establishing a trusting relationship where the elderly individual feels safe discussing their concerns can help alleviate feelings of anxiety and promote better hygiene practices.
Social interaction can also influence an elderly person's willingness to engage in personal hygiene. Isolation can lead to neglect of self-care, as the individual may feel there is no one to impress or no reason to maintain cleanliness. Encouraging social activities, whether through family visits, community programs, or group outings, can motivate older adults to take pride in their appearance and hygiene.
Lastly, education and awareness are vital in addressing hygiene resistance. Caregivers and family members should educate themselves about the common challenges faced by the elderly regarding hygiene. This knowledge will enable them to provide the right support and resources to make personal care more manageable. For instance, understanding the importance of skin care can help prevent issues like bedsores, which are prevalent in individuals with limited mobility.
In conclusion, dealing with "hygiene resistance" in the elderly requires a multifaceted approach that encompasses physical, cognitive, emotional, and social aspects. By recognizing the underlying factors contributing to hygiene issues and employing effective strategies, caregivers can significantly improve the quality of life for older adults. Promoting dignity and self-respect through proper hygiene practices is essential for the overall health and happiness of the elderly population.