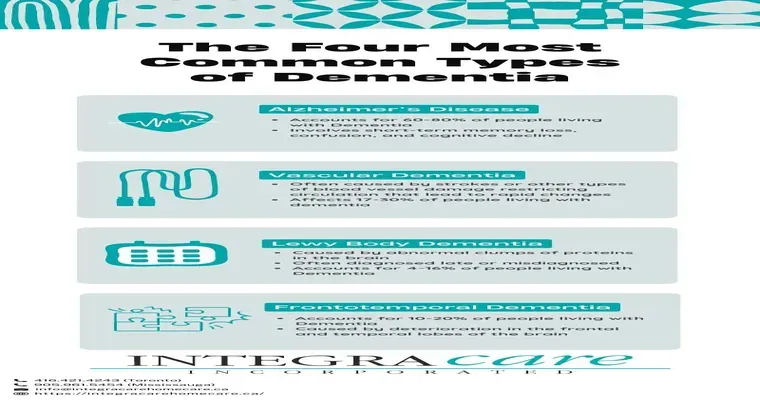
Dementia is a broad term used to describe a range of "cognitive decline" disorders that affect memory, thinking, and social abilities. This condition is not just a natural part of aging; it encompasses various diseases, including "Alzheimer's disease", vascular dementia, and Lewy body dementia. As individuals experience cognitive decline, the impact on their daily lives can be profound, leading to challenges in communication, decision-making, and even performing routine tasks. Understanding dementia is crucial for caregivers, families, and communities to provide support and improve the quality of life for those affected.
The onset of dementia often starts subtly. Family members may notice small changes in memory or behavior, such as forgetting recent events or struggling to find the right words during conversations. These early signs can be easily overlooked or attributed to normal aging. However, as dementia progresses, the "cognitive decline" becomes more pronounced, leading to significant disruptions in daily functioning.
One of the most challenging aspects of witnessing cognitive decline is the emotional toll it takes on both the individual and their loved ones. Individuals may experience feelings of frustration, confusion, and sadness as they grapple with their changing abilities. Family members often feel helpless as they watch someone they love begin to lose their identity and independence. Providing support during this time requires patience, understanding, and a willingness to adapt to new communication methods and care strategies.
Diagnosis of dementia typically involves a comprehensive assessment by a healthcare professional, including a medical history review, cognitive tests, and sometimes brain imaging. Early diagnosis can be beneficial, as it allows for the development of care plans and potential treatments that may slow the progression of the disease. Awareness of the symptoms and seeking help promptly can lead to better outcomes.
There are several types of dementia, each with unique characteristics and progression patterns. "Alzheimer's disease" is the most common form, characterized by a gradual decline in memory and cognitive function. Vascular dementia, on the other hand, often results from reduced blood flow to the brain and may follow a more stepwise progression. Understanding these differences is essential for effective management and support.
Support for individuals experiencing dementia can take many forms. Creating a safe and structured environment is crucial, as individuals may struggle with disorientation and confusion. Engaging in cognitive activities, maintaining social connections, and incorporating physical exercise can also help slow cognitive decline and improve overall well-being. Additionally, caregivers should prioritize self-care, as the demands of caregiving can lead to burnout and emotional distress.
In conclusion, witnessing cognitive decline due to dementia can be a heart-wrenching experience for both the individual and their loved ones. By recognizing the signs, seeking early diagnosis, and providing compassionate support, families and caregivers can navigate the challenges of dementia together. Understanding the various forms of dementia and their impact on cognitive function is essential in fostering a supportive environment that honors the dignity and needs of those affected.