"Hematuria", the presence of "blood in urine", is a significant health concern that often affects the "elderly population". As individuals age, they become increasingly susceptible to various medical conditions, making it essential to understand the causes, implications, and treatment options for hematuria in older adults. This article will explore the potential causes of hematuria, its symptoms, diagnostic procedures, and possible treatment methods to help manage this condition effectively.
Understanding Hematuria
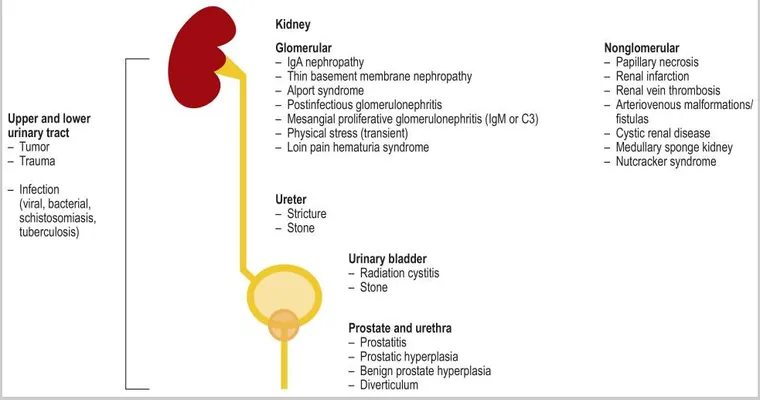
Hematuria can be classified into two categories: "gross hematuria" and "microscopic hematuria". Gross hematuria involves visible blood in urine, while microscopic hematuria can only be detected under a microscope. Both types can occur for various reasons, and identifying the underlying cause is crucial for effective treatment.
Common Causes of Hematuria in the Elderly
Several factors can contribute to hematuria in elderly individuals. Some of the most common causes include:
1. "Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs)": Infections can lead to inflammation and bleeding in the urinary tract, resulting in hematuria.
2. "Kidney Stones": These hard deposits can cause irritation and bleeding in the urinary system.
3. "Enlarged Prostate": Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) is common in older men and can lead to hematuria.
4. "Bladder or Kidney Tumors": Both benign and malignant tumors can cause blood in the urine.
5. "Glomerulonephritis": This inflammation of the kidney's filtering units can result in hematuria.
6. "Trauma or Injury": Falls or accidents can lead to internal injuries that cause bleeding.
Symptoms to Watch For
While hematuria is the primary symptom, it is essential to be aware of accompanying signs that may indicate a more serious condition. These can include:
Pain or burning sensation during urination
Increased frequency of urination
Abdominal or back pain
Fever or chills
Unexplained weight loss
If any of these symptoms are present alongside hematuria, it is crucial to seek medical attention promptly.
Diagnosis of Hematuria
To diagnose the cause of hematuria, healthcare providers typically conduct a thorough evaluation, which may include:
A detailed medical history and physical examination
Urinalysis to detect blood cells, proteins, and signs of infection
Imaging tests such as ultrasounds, CT scans, or MRIs to visualize the urinary tract
Cystoscopy, where a thin tube with a camera is inserted into the bladder to look for abnormalities
Treatment Options
The treatment for hematuria in the elderly largely depends on its underlying cause. Some common approaches include:
"Antibiotics" for urinary tract infections
"Medications" to manage prostate enlargement
"Surgical procedures" to remove kidney stones or tumors
"Corticosteroids" for inflammatory conditions like glomerulonephritis
Conclusion
Hematuria in the elderly is a condition that should not be overlooked. With various potential causes, it is essential for older adults and their caregivers to remain vigilant about urinary health. Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment can greatly improve outcomes and quality of life for those affected. If you or a loved one experiences hematuria, do not hesitate to consult a healthcare professional for a comprehensive evaluation and management plan.