If you are experiencing "chronic pain", you may be surprised to learn that your "brain" plays a crucial role in how you perceive discomfort. Understanding the connection between your brain and pain can lead to better management strategies, improving your overall quality of life. This article will explore the intricate relationship between the brain and pain, and how this knowledge can empower you in your healing journey.
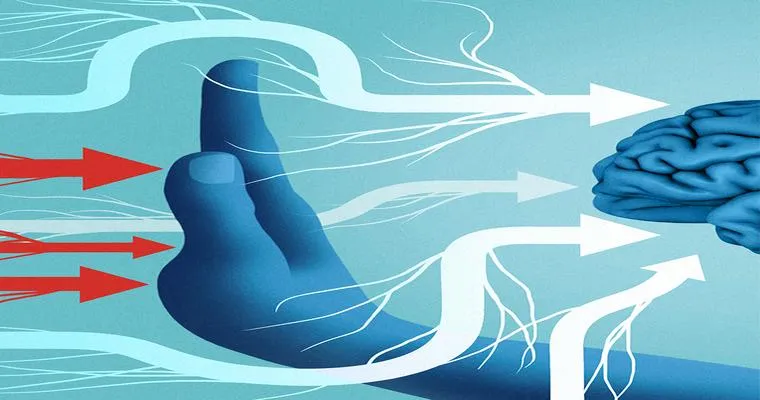
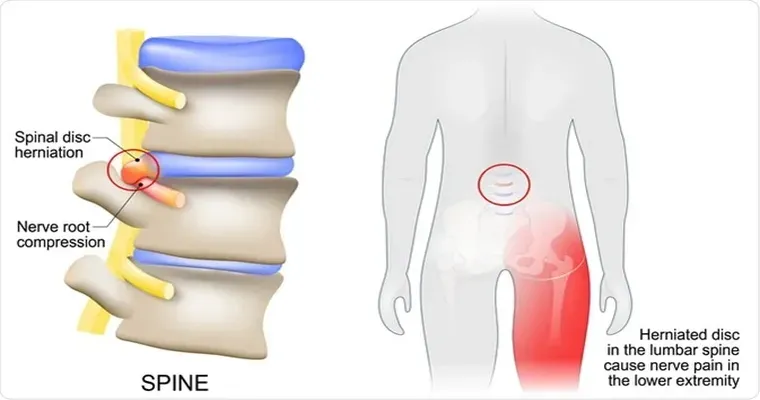
Pain is not merely a physical sensation; it is a complex experience that involves various systems in your body, particularly the "nervous system" and the "brain". When you sustain an injury or experience inflammation, your body sends signals to your brain through the nervous system. The brain processes these signals and interprets them as pain. However, this process can be influenced by several factors, including emotional state, previous experiences, and even beliefs about pain.
Recent research has shown that the brain can sometimes amplify pain signals, leading to a condition known as "central sensitization". This phenomenon occurs when the brain becomes overly responsive to pain stimuli, causing even minor aches to feel unbearable. It can be particularly common in individuals with conditions such as fibromyalgia or chronic fatigue syndrome, where the body is in a state of heightened sensitivity.
Understanding that your "brain" has the power to modulate pain can be a game-changer. It opens up new avenues for pain relief that go beyond traditional medication. Techniques such as "mindfulness", "cognitive-behavioral therapy", and "neurofeedback" can help retrain the brain's response to pain. These methods focus on changing how the brain interprets pain signals, offering a holistic approach that addresses both the physical and psychological aspects of pain.
Moreover, lifestyle choices play a significant role in how your brain processes pain. Regular "exercise", a balanced diet, and adequate sleep can enhance your brain's resilience against pain. Activities like yoga and meditation not only promote physical well-being but also contribute to mental clarity and emotional stability, further influencing pain perception.
In conclusion, if you find yourself in pain, it may be time to shift your focus from the physical aspect to the neurological mechanisms at play. By understanding the profound influence of the "brain" on "pain", you can explore effective strategies to manage your discomfort. Remember, pain is not just a signal of injury; it is a complex interplay of bodily functions that you can learn to navigate with the right knowledge and tools.