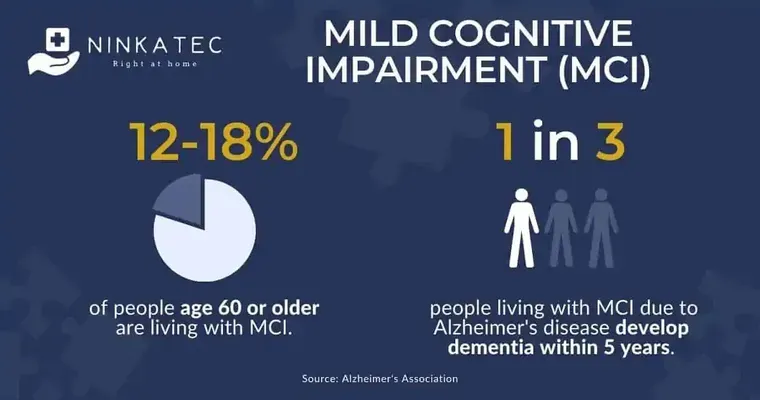
"Mild Cognitive Impairment" (MCI) is a significant health concern that affects many individuals as they age. It is crucial to understand what MCI entails, its symptoms, potential causes, and its implications for future cognitive health. In this article, we will explore ten essential things to know about mild cognitive impairment, shedding light on this often-overlooked condition.
1. What is Mild Cognitive Impairment?
Mild Cognitive Impairment is a stage between normal age-related cognitive changes and more severe conditions like "Alzheimer's disease" or other types of dementia. Individuals with MCI experience noticeable changes in memory or cognitive function but can still perform routine daily activities.
2. Symptoms of MCI
The symptoms of mild cognitive impairment can vary, but they often include memory lapses, difficulty concentrating, and challenges in planning or organizing tasks. People may also notice issues with language, such as struggling to find the right words during conversations.
3. Risk Factors
Several risk factors can contribute to the development of MCI. Age is the most significant risk factor, with older adults being more susceptible. Other factors include a family history of dementia, cardiovascular diseases, and lifestyle choices such as smoking and physical inactivity.
4. Diagnosis of MCI
Diagnosing mild cognitive impairment typically involves a comprehensive evaluation by a healthcare professional. This assessment may include cognitive tests, medical history reviews, and brain imaging to rule out other conditions that could be causing cognitive decline.
5. Potential Causes of MCI
The exact causes of mild cognitive impairment are not fully understood. However, it is believed that changes in the brain, such as the buildup of "amyloid plaques" and "tau tangles", may play a role. Other factors such as inflammation and vascular issues may also contribute to MCI.
6. MCI and Dementia
While MCI increases the risk of developing dementia, not everyone with MCI will progress to this more severe condition. Some individuals may remain stable or even regain cognitive function over time. Early diagnosis and intervention are crucial in managing symptoms and potentially delaying progression.
7. Treatment Options
Currently, there are no specific medications approved for treating mild cognitive impairment. However, lifestyle changes, cognitive training, and social engagement can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life. Engaging in regular physical activity and maintaining a healthy diet may also support cognitive health.
8. Monitoring MCI
Regular monitoring is essential for individuals diagnosed with mild cognitive impairment. Routine follow-ups with healthcare providers can help track changes in cognitive function and adjust care plans as needed. This proactive approach can aid in early detection of any further decline.
9. Support for Individuals and Caregivers
Living with mild cognitive impairment can be challenging, not just for the individual but also for caregivers. Support groups and education can provide valuable resources and emotional support. Engaging in discussions with family and friends about the condition can foster understanding and assistance.
10. Importance of Awareness
Increasing awareness about mild cognitive impairment is vital for early diagnosis and intervention. Educating the public about the signs and symptoms can lead to better outcomes for individuals affected by MCI and potentially delay the onset of more severe cognitive decline.
In conclusion, understanding mild cognitive impairment is essential for those affected and their families. By recognizing the symptoms, risk factors, and potential treatments, individuals can take proactive steps towards managing their cognitive health. If you or a loved one are experiencing signs of MCI, consulting with a healthcare professional is a critical first step.