Diabetes is a "chronic condition" that affects millions of people worldwide. Understanding how to properly "test for diabetes" and the available "treatment options" is crucial for managing this disease effectively. With early detection, individuals can take proactive steps to control their blood sugar levels and prevent potential complications associated with diabetes.
Understanding Diabetes
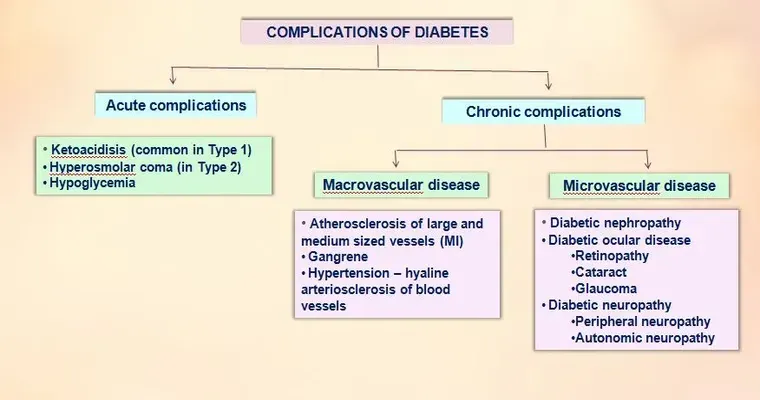
Diabetes occurs when the body cannot effectively use insulin, a hormone that regulates blood sugar. There are two main types of diabetes: Type 1 and Type 2. Type 1 diabetes is usually diagnosed in children and young adults, while Type 2 diabetes is more common in adults and is often linked to obesity and a sedentary lifestyle.
Testing for Diabetes
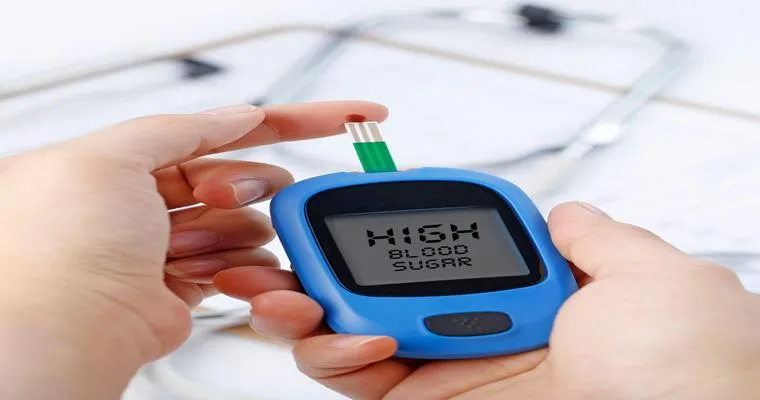
Testing for diabetes involves a series of "blood tests" that measure glucose levels. Here are the primary tests used:
1. "Fasting Blood Sugar Test": This test measures blood sugar levels after an overnight fast. A reading of 126 mg/dL or higher indicates diabetes.
2. "Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT)": This test involves fasting overnight and then drinking a sugary solution. Blood sugar levels are tested two hours later. A reading of 200 mg/dL or higher suggests diabetes.
3. "A1C Test": This blood test measures average blood sugar levels over the past two to three months. An A1C of 6.5% or higher indicates diabetes.
Regular testing is essential for individuals at risk of developing diabetes, such as those with a family history or those who are overweight.
Treating Diabetes
Once a diagnosis is made, effective treatment is vital for managing diabetes and maintaining a healthy lifestyle. Here are some common treatment options:
1. "Lifestyle Changes": One of the most effective ways to manage Type 2 diabetes is through lifestyle modifications. This includes adopting a "balanced diet", engaging in regular physical activity, and maintaining a healthy weight. Foods low in sugar and high in fiber can help control blood sugar levels.
2. "Medications": For those who cannot manage diabetes through lifestyle changes alone, medications may be necessary. These can include oral medications that help the body use insulin more effectively or insulin therapy itself for Type 1 diabetes.
3. "Monitoring Blood Sugar Levels": Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels is crucial to ensure they remain within target ranges. This can be done using home testing kits or continuous glucose monitors.
4. "Education and Support": Engaging with healthcare professionals, diabetes educators, and support groups can provide valuable information and motivation for managing diabetes effectively.
Conclusion
In summary, "testing for diabetes" and understanding the various "treatment options" are essential steps in managing this condition. By staying informed and proactive, individuals can lead healthy lives despite a diabetes diagnosis. Regular testing, lifestyle changes, medication, and support are key components that can make a significant difference in managing diabetes effectively. If you suspect you may be at risk, consult a healthcare professional for guidance and testing.