Alzheimer's disease significantly impacts the "cognitive function" of individuals, leading to various challenges, including difficulties with basic activities such as eating and swallowing. As the disease progresses, it becomes increasingly common for "Alzheimer's patients" to struggle with these essential tasks. Understanding why this occurs is crucial for caregivers and loved ones, as it can help them provide better support and care.
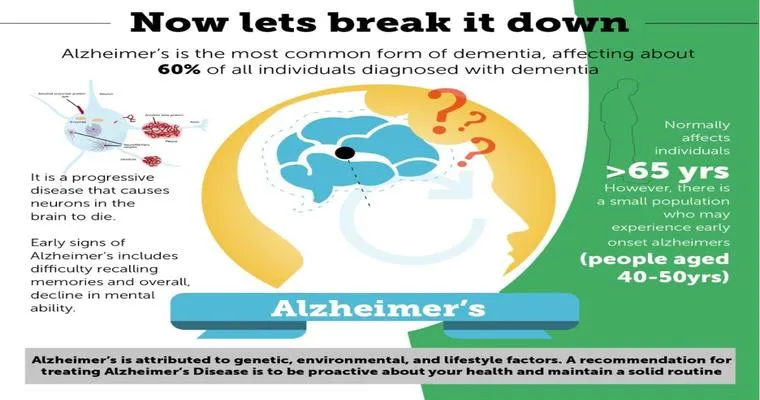
Alzheimer's disease primarily affects the brain regions responsible for "memory", "reasoning", and "motor skills". As neurons degenerate and the brain's structure changes, patients may experience confusion and forgetfulness regarding daily activities, including the process of eating. One of the critical areas affected is the "frontal lobe", which plays a vital role in planning and executing tasks. Consequently, patients may forget how to use utensils or may lose the ability to recognize food altogether.
In addition to cognitive decline, Alzheimer's patients often experience "dysphagia", a medical term for difficulty swallowing. This condition can arise due to weakened muscles in the throat and mouth, making it challenging for individuals to coordinate the complex actions required for swallowing. As the disease advances, the brain's ability to send signals to these muscles diminishes, resulting in an increased risk of choking and aspiration.
Another factor contributing to these issues is the "loss of interest in food". Many Alzheimer's patients may not recognize hunger or may forget to eat altogether. This lack of motivation can stem from various factors, including depression, sensory changes, or even the inability to recall the pleasure associated with eating. Caregivers may notice that their loved ones skip meals or eat less than they should, leading to weight loss and malnutrition.
Moreover, the "environment" in which Alzheimer’s patients eat can also impact their ability to consume food. A noisy or chaotic setting can be overwhelming and distracting. Patients may struggle to focus on the act of eating when there are multiple stimuli around them. Creating a calm and pleasant eating atmosphere can help enhance their experience and encourage them to eat.
To support Alzheimer's patients in maintaining proper nutrition, caregivers should adopt several strategies. First, it is essential to establish a consistent routine around meal times. Familiarity can provide comfort and help reinforce memory. Additionally, caregivers can simplify meals by offering finger foods, which are easier to handle and require less coordination than traditional meals. Using colorful plates and utensils can also stimulate interest and make food more appealing.
Lastly, regular check-ups with healthcare providers can help monitor any swallowing difficulties. Speech therapists can provide valuable assistance and exercises to improve swallowing skills. Caregivers should not hesitate to seek professional guidance if they notice significant changes in eating habits or swallowing abilities.
In summary, understanding why "Alzheimer's patients" forget how to eat or swallow is vital for effective caregiving. The combination of cognitive decline, physical challenges, and changes in interest can create barriers to proper nutrition. With appropriate strategies and support, caregivers can help ensure that their loved ones receive the nourishment they need, promoting their overall well-being and quality of life.