Navigating "Medicaid" benefits and skilled nursing care can be overwhelming, especially when you find yourself in a situation where you can’t make "house payments". Many individuals and families face the challenge of managing long-term care costs while trying to maintain their homes. Understanding how "Medicaid" works in relation to "skilled nursing" and the implications for your home can help you make informed decisions during a difficult time.
Understanding Medicaid and Skilled Nursing
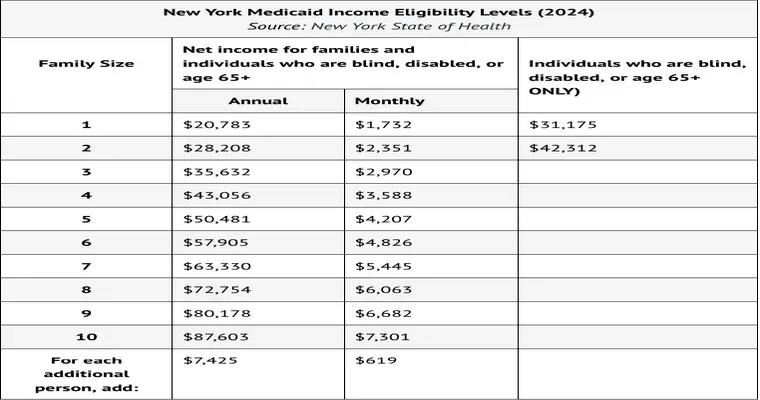
"Medicaid" is a state and federally funded program designed to provide healthcare coverage for low-income individuals, including those who require "skilled nursing" care. This type of care is often necessary for people with chronic illnesses or disabilities who need assistance with daily living activities. Under Medicaid, eligible individuals can receive coverage for various services, including "nursing home care", rehabilitation, and personal care services.
The Financial Implications of Skilled Nursing
When considering skilled nursing under "Medicaid", it's essential to understand how your financial situation will be impacted, particularly regarding your "house payments". If you are unable to make these payments due to the high costs associated with long-term care, there are several factors to consider:
1. "Asset Limits": Medicaid has specific asset limits that determine eligibility for the program. If your assets exceed these limits, you may not qualify for benefits. However, there are exemptions, including your primary residence, which may not count against your asset limit.
2. "Income Considerations": Your income will also be assessed when applying for "Medicaid". If your income is low due to high medical expenses, you may still qualify for benefits that can ease the burden of "skilled nursing" costs.
3. "Home Equity": If you own a home, its equity may affect your eligibility for "Medicaid". However, if you reside in the home and it is considered your primary residence, it is typically exempt from being counted as an asset, allowing you to maintain ownership while receiving care.
Options for Homeowners Facing Financial Strain
If you cannot make "house payments" due to the financial strain from skilled nursing care, consider these options:
1. "Refinancing Your Mortgage": If you have equity in your home, refinancing may lower your monthly payments, making them more manageable. This can provide some financial relief as you navigate your healthcare needs.
2. "Reverse Mortgage": For those over 62, a reverse mortgage may be an option. This allows you to convert part of your home equity into cash, which can be used to cover "skilled nursing" expenses while allowing you to stay in your home.
3. "Seek Financial Counseling": Consulting with a financial advisor or counselor who specializes in elder care can help you explore your options. They can provide guidance on managing your assets, applying for "Medicaid", and understanding your rights regarding home ownership.
Conclusion
Dealing with the challenges of paying for "skilled nursing" care under "Medicaid" while trying to maintain your home can be daunting. However, understanding your options and the rules surrounding "Medicaid" can empower you to make informed choices. If you find yourself unable to meet "house payments", consider seeking professional advice to explore solutions that can alleviate financial stress while securing the care you need.