Understanding "prescription drug coverage" under "Medicaid" is crucial for individuals who rely on this program for their healthcare needs. Medicaid provides essential health services to millions of low-income individuals and families, including coverage for necessary medications. This article will delve into the specifics of how Medicaid handles prescription drug coverage, the benefits it offers, and the eligibility requirements for beneficiaries.
Medicaid is a joint federal and state program designed to assist those with limited income and resources. Each state administers its own Medicaid program, which means that "prescription drug coverage" can vary significantly from one state to another. However, all state Medicaid programs must comply with federal regulations that ensure essential medications are covered.
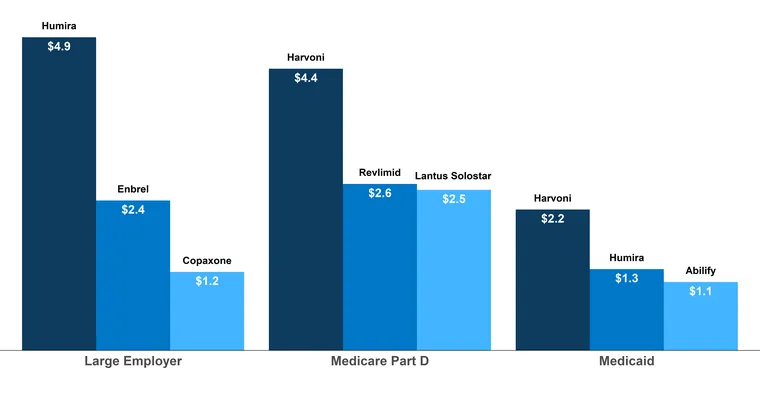
One of the key components of "prescription drug coverage" under Medicaid is the "formulary", which is a list of medications that are approved for use under the program. States are required to provide access to a wide range of medications, including both generic and brand-name drugs. The formulary typically includes drugs that are necessary for treating various medical conditions, and states must review and update their formularies regularly to ensure they meet the needs of their beneficiaries.
In addition to the formulary, Medicaid beneficiaries often have access to a "pharmacy network", which includes pharmacies that accept Medicaid. This network allows individuals to fill their prescriptions at various locations, making it easier to access needed medications. Some states may also offer mail-order options for prescription drugs, providing added convenience for those who prefer to receive their medications by mail.
Eligibility for Medicaid and its "prescription drug coverage" is determined by several factors, including income, household size, and specific state guidelines. Most states use the "Federal Poverty Level" as a benchmark to determine eligibility. Individuals must meet income requirements to qualify, which can differ based on their family size and the state in which they reside.
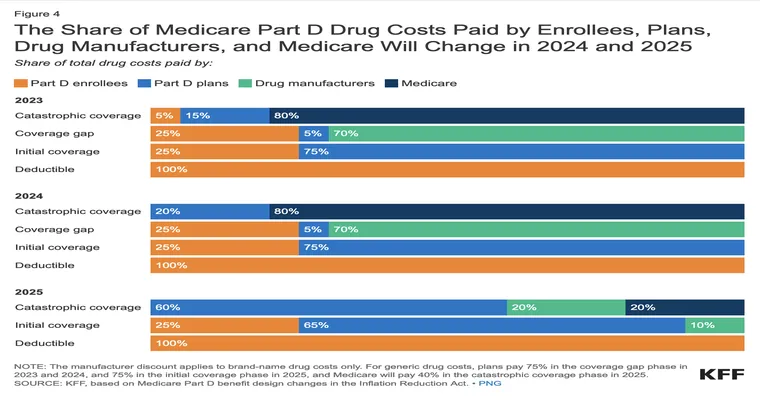
For those who qualify for Medicaid, the program generally covers the cost of prescription medications with minimal out-of-pocket expenses. Some states may implement copayments for certain drugs, but these amounts are typically low, ensuring that essential medications remain affordable for beneficiaries.
In addition to traditional Medicaid, there are programs such as "Medicaid Managed Care", which may offer additional benefits, including enhanced access to prescription drug coverage. Managed care plans often negotiate directly with pharmaceutical companies to secure better pricing on medications, which can result in lower costs for beneficiaries.
For individuals who are unsure about their eligibility for Medicaid or have questions about their "prescription drug coverage", it is advisable to contact their state Medicaid office or visit their official website. These resources can provide valuable information about available benefits, the application process, and any changes to coverage that may occur.
In conclusion, "prescription drug coverage for Medicaid" is an essential component of the program that enables millions to access necessary medications. By understanding the specifics of coverage, eligibility requirements, and available resources, beneficiaries can better navigate the complexities of Medicaid and ensure they receive the healthcare services they need.