
Selected reviews about elderly care communities
Selected reviews about elderly care communities offer valuable insights into the experiences of residents and their families. These reviews can highlight the strengths and weaknesses of different communities, helping you make an informed decision when choosing the right care for your loved one.
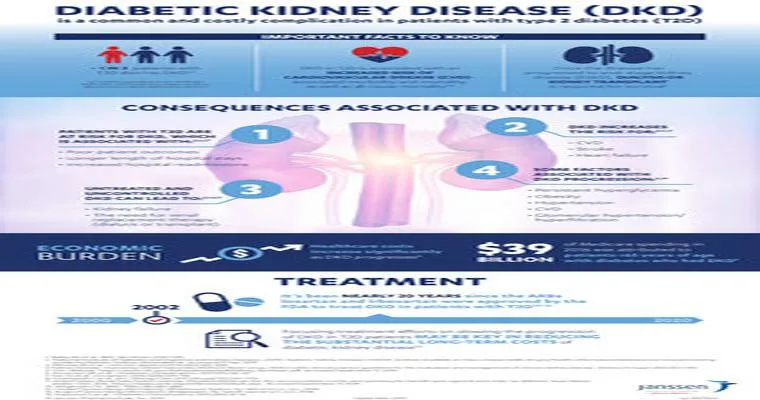
Type 2 Diabetes: Kidney Complications
Type 2 diabetes can lead to kidney complications, primarily diabetic nephropathy, which damages the kidneys over time. This condition impairs their ability to filter waste from the blood, potentially resulting in kidney failure. Managing blood sugar levels is crucial to prevent or slow the progression of kidney-related issues.

Who Gets Diabetes? Top 10 Risk Factors
Diabetes can affect anyone, but certain risk factors increase susceptibility. Key contributors include genetics, obesity, inactivity, age, and poor diet. Additionally, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, gestational diabetes, and certain ethnic backgrounds also play a role. Understanding these factors can help in prevention and management strategies.
Testing for Diabetes and Treating It
Testing for diabetes typically involves measuring blood sugar levels through fasting tests, oral glucose tolerance tests, or A1C tests. Treatment focuses on lifestyle changes, including diet and exercise, along with medications like insulin or oral hypoglycemics. Regular monitoring and education are essential for effective management and prevention of complications.

Pre-Diabetes: What You Need to Know
Pre-diabetes is a critical health condition where blood sugar levels are higher than normal but not yet high enough for a diabetes diagnosis. It often leads to type 2 diabetes if unmanaged. Awareness, lifestyle changes like improved diet and increased physical activity, and regular monitoring can help prevent progression.
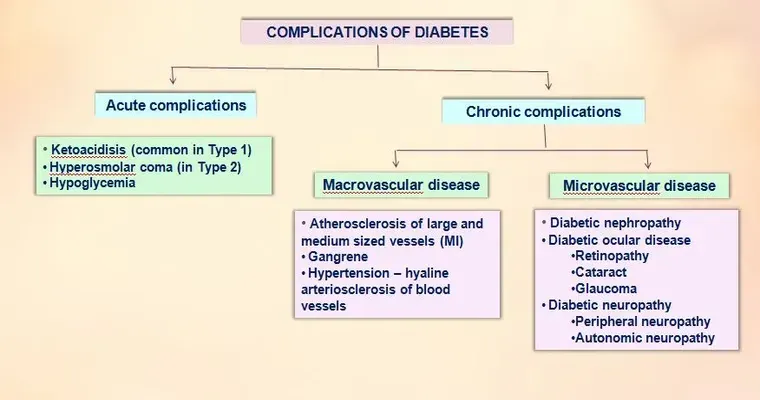
5 Common Complications from Diabetes
Diabetes can lead to several complications, including cardiovascular disease, which increases the risk of heart attacks and strokes. Neuropathy may cause nerve damage, resulting in pain and numbness. Kidney damage can lead to renal failure, while vision problems like retinopathy threaten eyesight. Additionally, poor circulation can result in foot infections and ulcers.
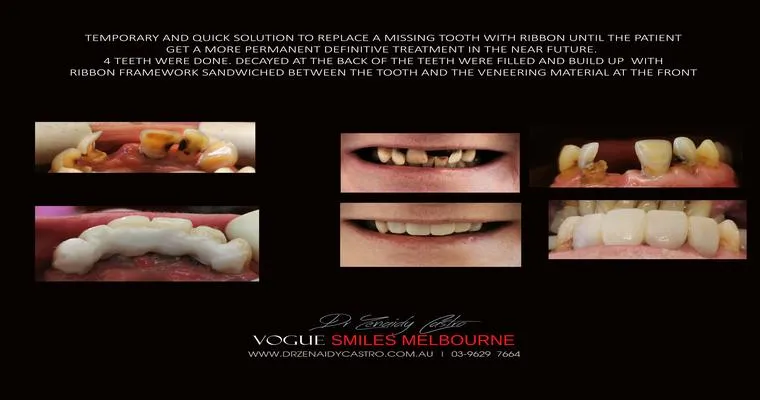
I need ideas for adjusting to permanent dentures, or learning how to live without teeth?
Adjusting to permanent dentures or living without teeth can be challenging but manageable. Focus on practicing speaking and eating with your new dentures, explore soft food options, and maintain good oral hygiene. Seek support from dental professionals and connect with others who have undergone similar experiences for tips and encouragement.

My 84 yr. old mom has LBD.
My 84-year-old mom is living with Lewy Body Dementia, a condition that affects her cognitive abilities and daily functioning. She experiences fluctuations in alertness, visual hallucinations, and movement difficulties. Despite these challenges, we cherish our moments together, finding joy in simple activities and maintaining a strong bond through love and support.

Suggestions on dealing with my 96 yr old mother refusing dental care?
Approach the situation with empathy and patience. Discuss her concerns, highlighting the importance of dental care for overall health. Involve her in the decision-making process, consider involving a trusted healthcare professional for support, and explore alternative options like in-home care or gentle dental services to make her feel more comfortable.
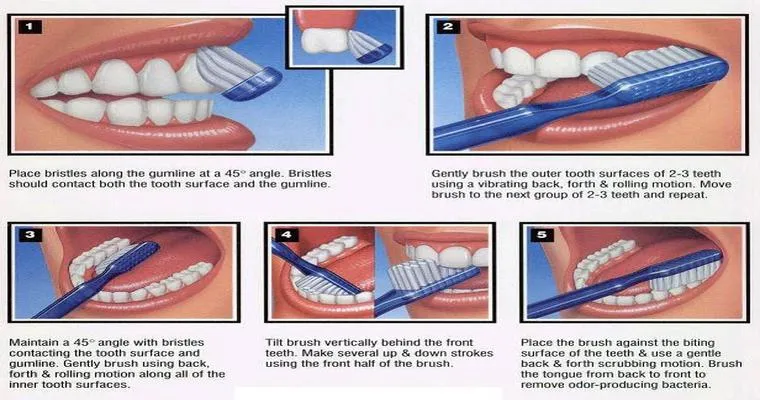
How do you facilitate teeth brushing?
To facilitate teeth brushing, create a routine by encouraging children to brush twice daily. Provide a fun, colorful toothbrush and flavored toothpaste to make the experience enjoyable. Demonstrate proper techniques, such as brushing in circular motions, and use a timer or music to ensure they brush for the recommended two minutes.
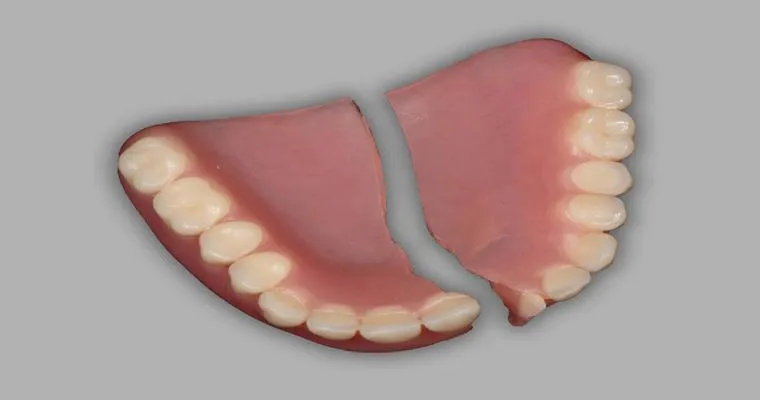
Broken denture, now what?
A broken denture can cause discomfort and difficulty in eating or speaking. It’s essential to avoid attempting DIY repairs, as this may worsen the damage. Instead, schedule an appointment with a dental professional who can assess the situation and recommend the best course of action, whether it’s repair or replacement.
My 67 year old hubby won’t wear his false teeth!
My 67-year-old husband refuses to wear his false teeth, insisting they feel uncomfortable and unnatural. This has become a source of frustration for both of us as he struggles with eating and speaking. I worry about his confidence and health, hoping he'll eventually embrace them for a better quality of life.
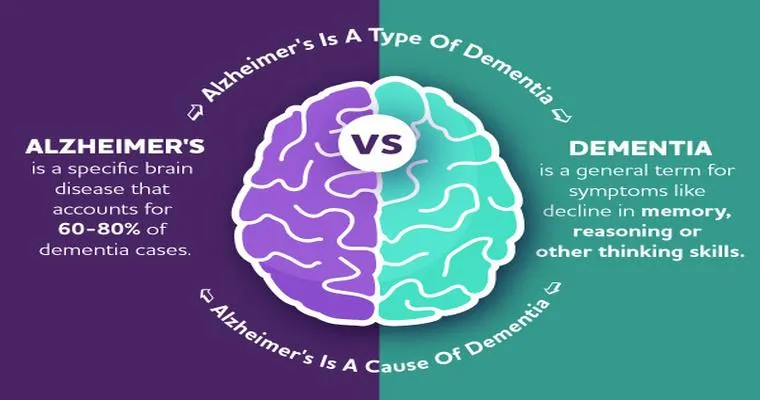
Have they found the cause of Alzheimer's?
Research into the causes of Alzheimer's disease continues to evolve, with scientists identifying various factors such as genetic predispositions, protein buildup, and inflammation in the brain. While significant progress has been made, a definitive cause remains elusive, underscoring the complexity of the disease and the need for further investigation.
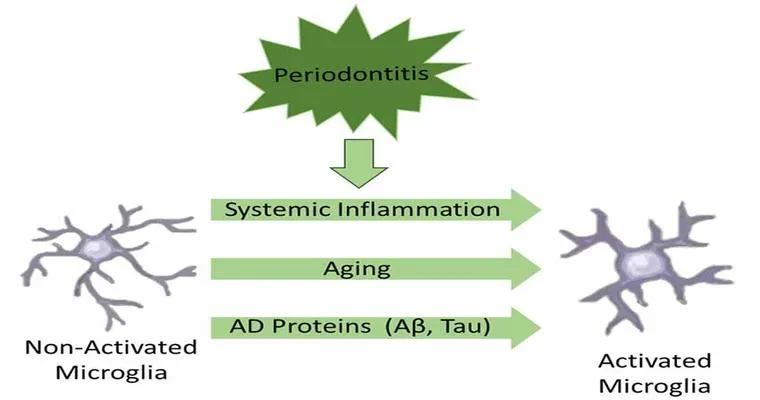
Have you been reading the articles about gum disease and dementia?
Recent articles suggest a potential link between gum disease and dementia, highlighting how oral health may influence cognitive decline. Researchers are exploring how inflammation from periodontal issues might affect brain health, prompting a deeper understanding of the connection between oral hygiene and neurological conditions, emphasizing the importance of maintaining good dental care.

Coping with Guilt and Regret
Coping with guilt and regret involves acknowledging feelings, reflecting on their causes, and understanding that everyone makes mistakes. Practicing self-compassion and seeking support from others can help in processing these emotions. Engaging in positive actions and making amends fosters healing and promotes personal growth, allowing for a healthier mindset.
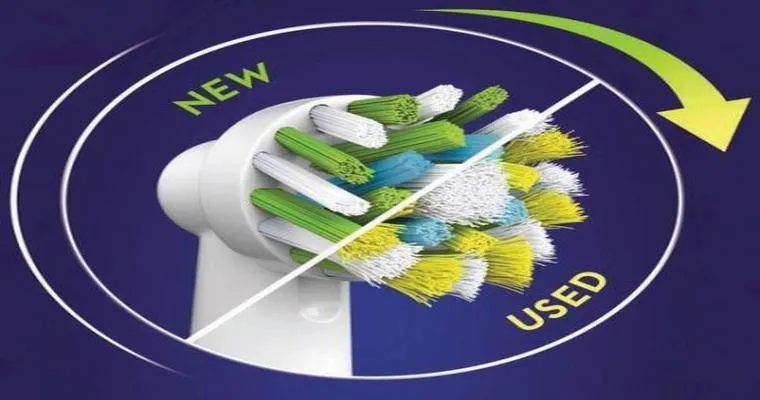

Heads up on monitoring oral hygiene
Maintaining oral hygiene is essential for overall health. Regular brushing and flossing prevent cavities and gum disease, while routine dental check-ups ensure early detection of issues. Additionally, monitoring dietary habits and limiting sugary snacks contribute to better oral health. Staying informed about proper care techniques can foster a brighter, healthier smile.
The lady with the wisdom tooth extraction at 76.
At 76, she faced the daunting prospect of wisdom tooth extraction, a procedure often associated with youth. Undeterred, she approached it with humor and grace, reflecting on a life filled with challenges. Her resilience and wisdom shone through, reminding everyone that age is just a number when confronting life's hurdles.
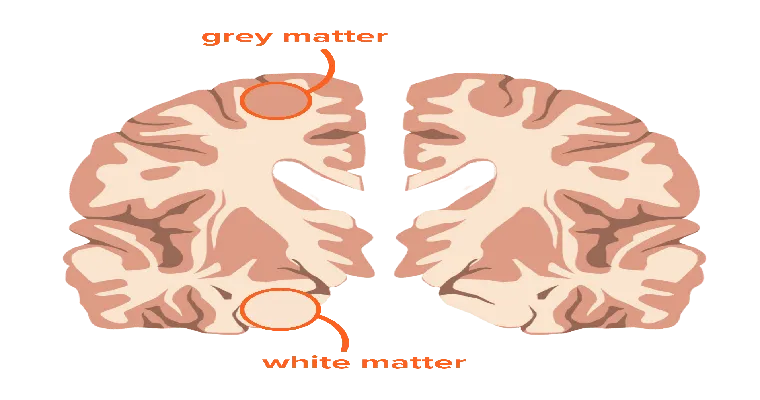
What Is Vascular Dementia?
Vascular dementia is a decline in cognitive function caused by reduced blood flow to the brain, often resulting from strokes or other vascular issues. Symptoms may include memory loss, confusion, and difficulty with problem-solving and planning. It is the second most common type of dementia after Alzheimer’s disease.

Warning Signs of Depression in the Elderly
Depression in the elderly can manifest through various warning signs, including persistent sadness, withdrawal from social activities, changes in appetite or sleep patterns, fatigue, and difficulty concentrating. It's essential to recognize these signs early, as they can significantly impact the individual's quality of life and overall well-being.
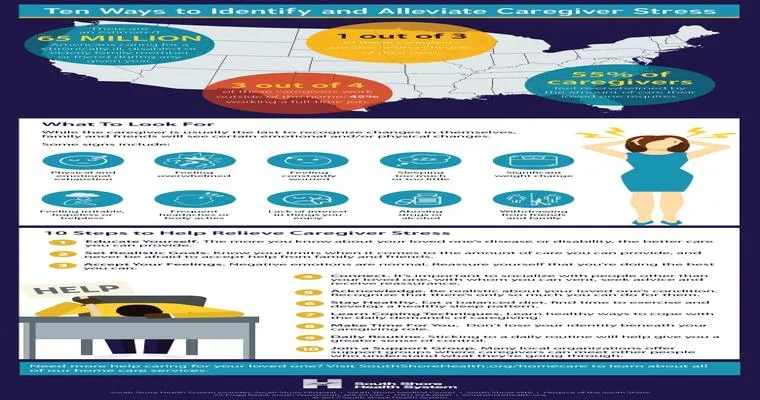
10 Ways to Prevent Caregiver Depression
Preventing caregiver depression involves prioritizing self-care, seeking support from friends and family, setting realistic expectations, and taking regular breaks. Engaging in physical activity, pursuing hobbies, and maintaining a healthy diet also contribute to emotional well-being. Additionally, accessing professional help when needed can significantly enhance resilience and overall mental health.
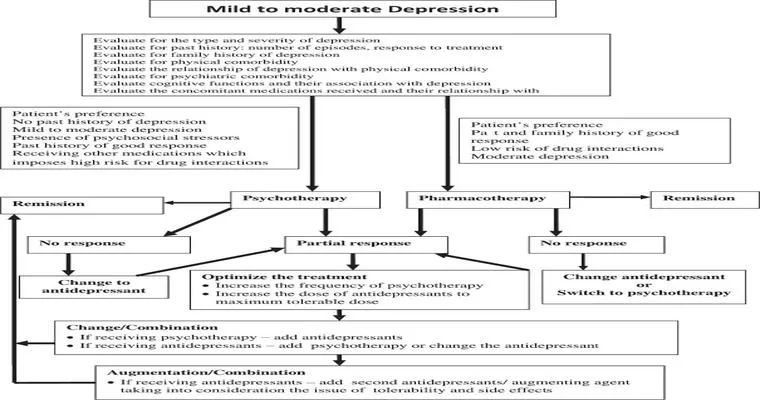
Treatments for Depression in the Elderly
Treatments for depression in the elderly typically include a combination of psychotherapy, medication, and lifestyle changes. Cognitive-behavioral therapy and interpersonal therapy are effective, while antidepressants may help manage symptoms. Regular physical activity, social engagement, and a healthy diet also play crucial roles in improving mental well-being in older adults.
Page 92 of 134