
Selected reviews about elderly care communities
Selected reviews about elderly care communities offer valuable insights into the experiences of residents and their families. These reviews can highlight the strengths and weaknesses of different communities, helping you make an informed decision when choosing the right care for your loved one.
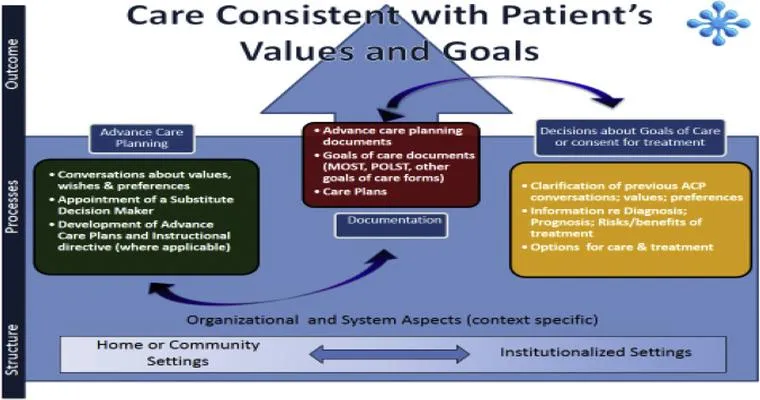
Deciding on an End of Life Plan
Deciding on an end-of-life plan involves thoughtful consideration of personal values, medical preferences, and legal arrangements. It encourages open discussions with family and healthcare providers to ensure wishes are respected. This process can bring peace of mind and clarity, fostering a sense of control during challenging times.

Vermont Passes Landmark Legislation Legalizing Physician-Assisted Suicide
Vermont has enacted groundbreaking legislation allowing physician-assisted suicide, making it one of the first states to legalize this practice. The law enables terminally ill patients to seek medical assistance in ending their lives, emphasizing patient autonomy and compassionate care. Advocates celebrate this as a significant step toward end-of-life rights.

Assisted Suicide and Elders: How Far Would a Loving Caregiver Go?
This exploration examines the complex ethical dilemmas faced by caregivers of elderly individuals considering assisted suicide. It delves into the emotional struggles, the balance between compassion and moral responsibility, and the impact of personal beliefs on decisions, highlighting the profound challenges of providing loving care in such sensitive circumstances.
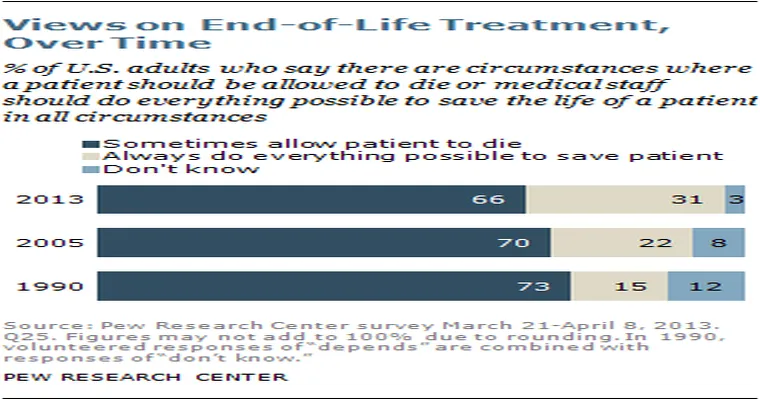
My Final Exit: Starvation or Assisted Suicide?
"My Final Exit: Starvation or Assisted Suicide?" explores the complex ethical dilemmas surrounding end-of-life choices. It examines the motivations behind individuals' decisions to forgo sustenance or seek assistance in dying, highlighting personal narratives, societal implications, and the ongoing debate about autonomy, dignity, and the right to choose one's own death.

Assisted Dying: Merciful or an Affront to the Value of Life?
Assisted dying raises profound ethical questions, balancing compassion for those suffering with the sanctity of life. Advocates argue it offers a dignified choice for terminal illness, while opponents believe it undermines the intrinsic value of life and could lead to potential abuses. The debate continues to evoke strong emotions on both sides.

When Is a Primary Residence Exempt From Medicaid?
A primary residence may be exempt from Medicaid eligibility considerations if it meets specific criteria, such as being occupied by the beneficiary, having a value below a certain limit, or being owned by a spouse or dependent. Special rules also apply for individuals with disabilities and elderly beneficiaries.
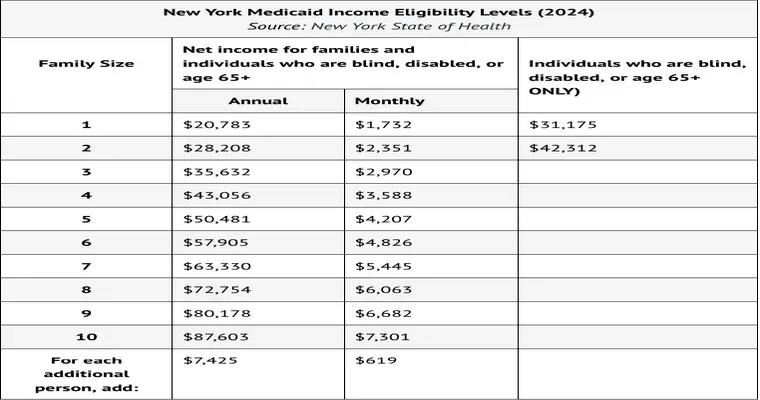
Asset Limits for Medicaid Eligibility
Asset limits for Medicaid eligibility refer to the maximum value of resources an individual can possess while still qualifying for benefits. These limits vary by state and program, typically excluding essential items like a primary home and personal belongings, ensuring that low-income individuals can access necessary healthcare services.

Understanding the Medicaid Look-Back Period and Penalty Period
The Medicaid Look-Back Period is a time frame, typically five years, during which asset transfers are reviewed to determine eligibility for benefits. If assets were given away or sold below market value, a Penalty Period may be imposed, delaying access to Medicaid services based on the value of those transfers.

How Joint Bank Accounts Affect Medicaid Eligibility
Joint bank accounts can impact Medicaid eligibility by potentially counting the combined assets of both account holders. If one account holder is applying for Medicaid, the entire balance may be considered available resources, which could exceed the asset limit and affect eligibility for benefits. Careful planning is essential.

4 Key Things to Know about Trusts and Medicaid Planning
Trusts can protect assets from Medicaid spend-down requirements, allowing individuals to qualify for benefits while preserving wealth for heirs. Understanding the types of trusts and their implications is crucial. Timing is essential, as Medicaid has look-back periods. Proper planning ensures compliance with regulations and maximizes financial security for future needs.

How to Set Up a Miller Trust for Medicaid Eligibility
Setting up a Miller Trust involves creating a specific type of irrevocable trust to qualify for Medicaid benefits while retaining excess income. The trust must meet state requirements, with income deposited into it to ensure the individual’s income falls below Medicaid eligibility limits, allowing access to necessary long-term care services.
Every time my female client (98) gets up, there is an uncontrollable stream of urine. Is there a medicine that would help?
A 98-year-old female client experiences uncontrollable urine leakage upon standing, which may indicate urinary incontinence. Various treatments, including medications like anticholinergics or beta-3 agonists, pelvic floor exercises, and lifestyle changes, can help manage her condition. It’s essential to consult a healthcare professional for a personalized assessment and treatment plan.
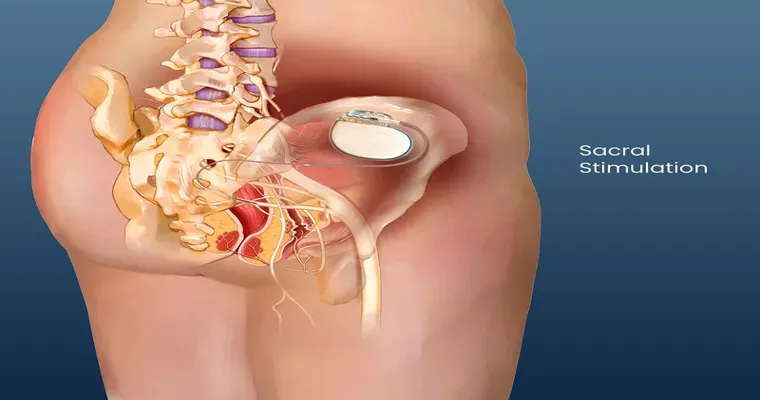
Experience with Sacral Neuromodulation?
Sacral neuromodulation is a minimally invasive treatment for bladder and bowel control issues. It involves implanting a device that stimulates the sacral nerves, improving communication between the bladder and brain. Patients often report significant relief from symptoms, enhancing quality of life. The procedure is generally safe with minimal side effects.

Bedridden grandmother with dementia is holding her urine. How can I stimulate her to not do this?
To help a bedridden grandmother with dementia who is holding her urine, create a comforting environment. Regularly encourage fluid intake and establish a consistent bathroom routine. Use gentle verbal cues and reminders, and consider using visual aids. Engage her in conversation to distract and relieve any anxiety about the situation.
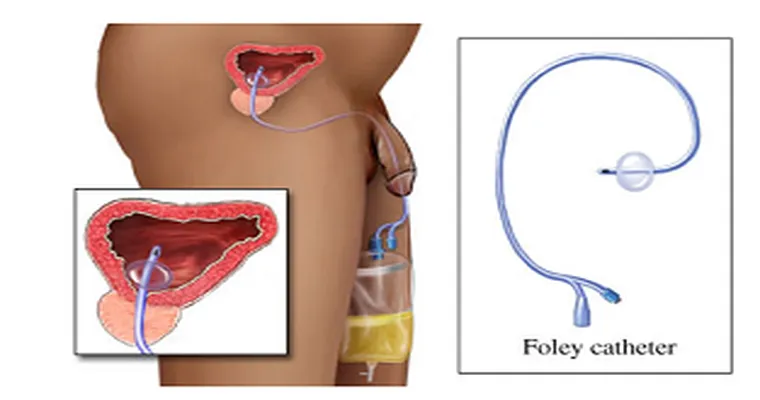
MIL has a Foley Catheter. Anyone know how often the urine bag should be cleaned?
A Foley catheter is a flexible tube inserted into the bladder to drain urine. It’s important to maintain hygiene to prevent infections. The urine bag should be cleaned regularly, typically every few days, and whenever it appears dirty. Always follow healthcare provider recommendations for specific cleaning protocols.

I have a small bladder and it's getting harder to find diapers in my size. Any ideas?
Finding the right size of diapers can be challenging, especially with a small bladder. It's important to explore options like specialized brands that cater to unique sizing needs. Online retailers often offer a wider variety, and joining support groups can provide recommendations and shared experiences from others facing similar issues.

How do I make my mom drink like she should?
Encourage your mom to stay hydrated by sharing fun and tasty drink ideas. Offer flavored water, herbal teas, or smoothies to make drinking enjoyable. Set reminders for her to sip throughout the day, and join her in the habit to create a supportive environment for better hydration.

Can POA be overridden?
A Power of Attorney (POA) can be overridden under certain circumstances. If the principal revokes the POA, a court determines the agent's authority, or if the principal becomes incapacitated, the POA may be invalidated. Additionally, a new POA can replace an existing one, effectively overriding it.
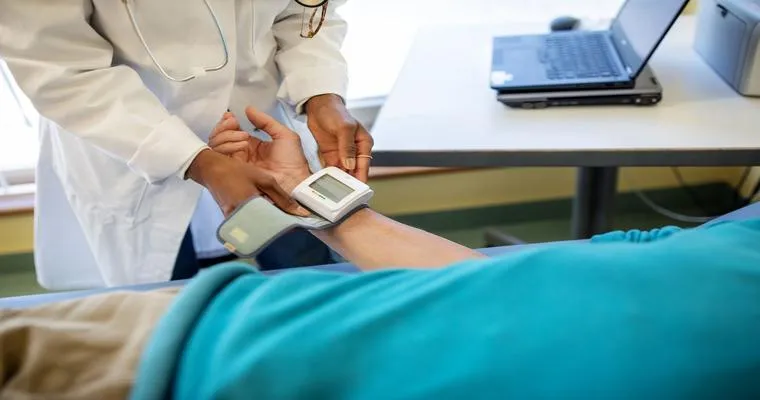
Will an electronic blood pressure machine give a false reading if the patient is lying down in bed?
An electronic blood pressure machine can give inaccurate readings if the patient is lying down. This position may affect blood flow and pressure, leading to lower measurements. For accurate results, it’s recommended that patients sit upright with their arm at heart level during the measurement process.
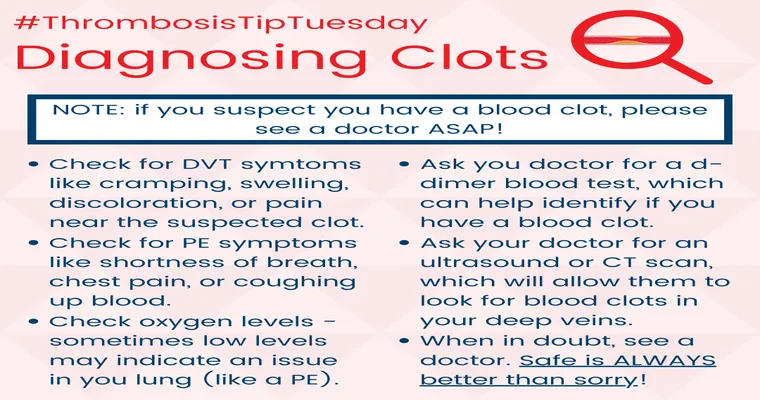
I need to know if anyone knows about blood clots?
I'm seeking information about blood clots and their implications. If anyone has knowledge or experience related to their causes, symptoms, or treatments, I would greatly appreciate your insights. Understanding this topic is important for health awareness, and any shared information would be helpful. Thank you for your assistance.
Page 116 of 134